The International Energy Agency expects worldwide EV sales to reach 14 million in 2023, and 28 million in 2024. They predict that by 2030 there will be 140 million electric cars on the road worldwide. Scientists, engineers, and manufacturers are developing new battery technology to meet demands—and to make EVs lighter, more efficient, more affordable, and be capable of faster charging.
Very simply put, lithium-ion batteries store and release energy via a chemical reaction. During this reaction, lithium ions move from one electrode to the other through a liquid electrolyte, either shedding or gaining electrons along the way. Run a current of electricity through the battery and it “charges.” Connect the terminals to a circuit and they discharge.
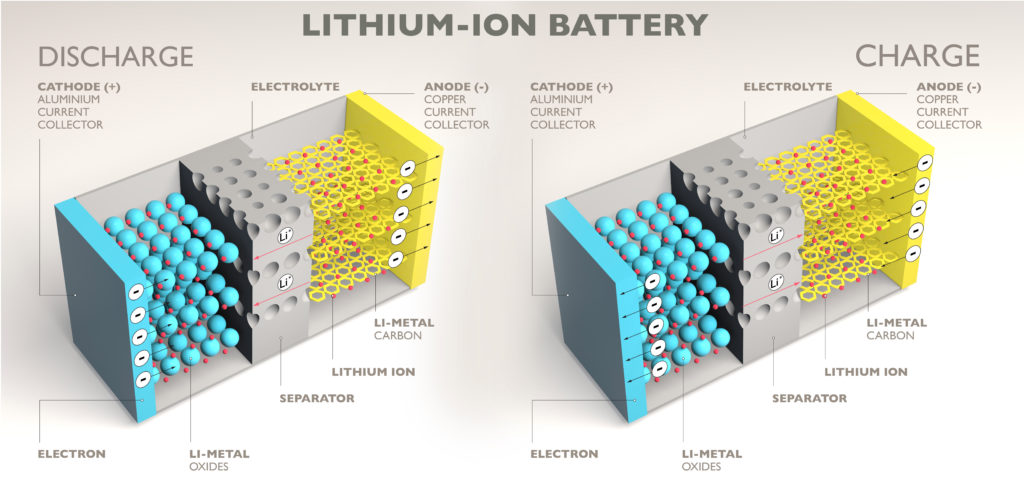
Commercial lithium-ion batteries contain a liquid or gel electrolyte. Solid-state lithium batteries use a solid electrolyte instead, reducing the overall size and weight of the batteries. Solid-state lithium batteries have several advantages over their liquid counterparts:
Solid-state lithium batteries have been in development since the mid-1970s, but they haven’t been made commercially available in large quantities. Recently Toyota and Honda have announced plans to manufacture solid-state batteries, along with US battery manufacturer QuantumScape. Toyota claims they developed a breakthrough in manufacturing and hope to produce EVs with solid-state lithium batteries as soon as 2025. Honda hope their new solid-state battery tech will reduce the weight of their batteries by up to 50%. QuantumScape recently announced they’ll be producing a 5Ah solid-state lithium battery that could be used in EV battery packs. The company claims the battery can endure 800 charge cycles without significant degradation.
Nissan have also recently announced their solid-state lithium battery project, which they claim will go online sometime in 2028. And in 2022 GM announced they’re investing $7 billion in solid-state battery tech.
Toyota claim their solid-state battery could give EVs a range of up to 1,200km (745 miles) and charge in about 10 minutes. Other manufacturers are promising similar range and charge times, but haven’t provided real-world data as of yet.
Most of today’s lithium-ion batteries use cobalt, an expensive and potentially dangerous element that’s only available in a few places on earth. Battery manufacturers are seeking alternatives to cobalt to avoid supply-chain interruptions and reduce costs. Many of the world’s largest cobalt mines in the Democratic Republic of Congo also have dangerous working conditions that endanger the lives of tens of thousands of miners. Reducing or eliminating the use of cobalt in lithium-ion batteries has many advantages. Lithium-sulfur batteries eliminate the need for cobalt or nickel, another rare element. They offer many benefits over lithium-cobalt batteries, including:
However, lithium-sulfur batteries face challenges like shorter cycle life and issues with sulfur’s stability. Researchers are actively working to overcome these obstacles and bring lithium-sulfur batteries to the mainstream EV market. Researchers at the Argonne National Laboratory recently announced a major breakthrough in lithium-sulfur battery chemistry, uncovering a key chemical process that stabilizes the sulfur cathode. The researchers hope they can refine the process to produce longer-lasting, more energy dense lithium-sulfur batteries in the future.
Lithium-ion batteries of all forms have been popular for decades due to their power density and power output. But alternative battery chemistries are gaining popularity as lithium ore becomes harder to mine and lithium supply lines are stressed by increasing demand. Sodium lies just below lithium on the periodic table and has similar properties, but it is far more common and easier to process. Sodium-ion batteries promise to deliver most of what lithium batteries deliver, but at a much lower cost.
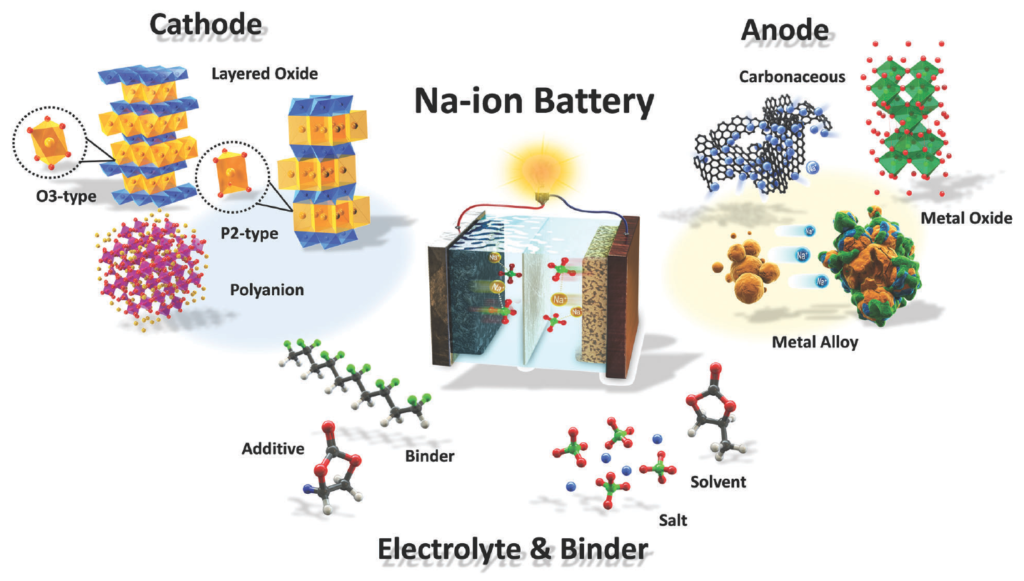
Sodium-ion batteries have been in development for more than 50 years, but they haven’t been commercially developed until recently. In the past, sodium-ion batteries weren’t able to match the energy density of lithium-ion batteries, were heavier, and deteriorated more quickly. Now some sodium-ion batteries are approaching the energy density of lithium-ion batteries and Chinese manufacturers CATL and BYD plan to release cars with sodium-ion batteries late in 2023. CATL plans to start mass-producing sodium-ion batteries in late 2023.
Sodium-ion batteries probably won’t replace lithium-ion batteries anytime soon, but they could be used in lower-cost EVs and for grid storage in the future.
Many next-generation batteries promise faster charging times than current batteries. Improving battery technology is crucial to improving charging times, making EVs more convenient for drivers everywhere. The world is rapidly building fast-charging infrastructure to ensure drivers can use their EVs for anything from daily commutes to road trips. The same fast-charging infrastructure will be crucial for electric commercial vehicles moving goods between cities.
At Tritium we work with EV manufacturers to ensure our chargers work flawlessly with the latest battery technology, conducting interoperability testing of vehicles at our facilities throughout the world. To learn more about our scalable, modular fast chargers, review our PKM150 fast chargers.
If you’re building the world’s fast-charging infrastructure, or if you’re interested in working with us to test your latest EVs before launching to the market, contact one of our experts today.
With Karim Farhat, Chief Commercial Officer, EVCS
Tritium is proud to feature our partner EVCS, one of the largest public EV charging networks on the US West Coast. Tritium supplies direct current (DC) fast chargers for the growing charging network. EVCS and Tritium are working together to help more people drive electric.
EVCS was founded in 2018 and has quickly become one of the largest and fastest-growing public EV charging networks on the US West Coast. EVCS’ mission is to accelerate access to affordable, reliable, and sustainable EV Charging. Powered by 100% renewable energy, EVCS develops, owns, and operates Level 2 and DC Fast charging stations that can be used by all EV models on the market today, including Tesla. EVCS has more than 850 chargers across more than 175 locations and continues to grow rapidly. In addition, EVCS offers EV drivers flexible subscription charging plans. This includes unlimited charging plans designed for gig and high-mileage drivers, with significant potential savings.
EV drivers prioritize several key factors when using our network and charging publicly in general. These include affordability, convenience of charging locations, and reliability. As a publicly accessible charging network, we always strive to optimize the customer experience across all three dimensions. We aim for charging sites that are safe and near attractive amenities. We work hard to ensure that every charger is available and those that are offline are rapidly repaired; and we continue to innovate with first-of-kind charging subscription plans and services that are cost-effective and appealing for a wide range of EV drivers with different needs. We’re committed to establishing EVCS as a trusted EV charging provider, ensuring that our customers have seamless and enjoyable charging experience.
EVCS offers a variety of charging services that are designed to fit the unique charging needs of a wide variety of EV drivers. Today, we offer four monthly subscription plans for regular and high-mileage drivers: Our most popular plan, Standard Anytime, includes 200 kWh monthly charging credit (about 720-780 miles range) for as low as $0.25/kWh. Essential Anytime is an entry-tier plan that includes 30 kWh of monthly charging credit (about 105-115 miles range) and is designed for drivers who might rely on EVCS’ public chargers less often. For high-mileage drivers, EVCS offers two very cost-effective charging plans: The Unlimited Anytime plan allows unlimited 24/7 access to any charger in the entire EVCS network, and Unlimited Off-Peak Pro allows similar unlimited access during nighttime. Enrolling in these plans helps EV drivers save significantly on their charging costs. Drivers can learn more and enroll at evcs.com/plans.
In addition, EVCS works with strategic partners to offer innovative charging plans that are customized to fit their drivers’ needs. Our partnership with Hertz on rideshare EV charging is a great example: Hertz rideshare renters in California get exclusive access to three price-competitive weekly charging plans. The EVCS + Hertz Rideshare Program is very successful, and we are excited to keep expanding our EV charging offerings through strategic partnerships.
DC Fast charging is critically important for EV drivers who may not have access to home charging. As EVs hit the mass-market, more prospective EV drivers, especially renters with no guaranteed and dedicated charging spots, need access to reliable and fast charging infrastructure. DC Fast chargers could be placed at destination locations such as public parking sites, grocery stores, shopping malls, gyms, and universities where people can charge while conducting their normal daily activities. DC Fast chargers can also work well at apartment complexes to benefit both residents and the public. In addition, DC Fast chargers are very beneficial near highways and major roads, to minimize range anxiety and meet the commuting needs of drivers; essentially aligning with people’s refueling habits at traditional gas stations. Today, EVCS installs and operates Tritium’s DC Fast chargers at all these locations to accommodate our customer needs. DC Fast charging makes electric vehicles a more viable and practical choice for a wider range of consumers, ultimately resulting in greater EV adoption.
The biggest challenges facing the industry today to build a fast-charging network are finding the best locations, reducing deployment timelines, and ensuring maximum network reliability. Installing a DC fast charger requires a large uptake of power capacity from the grid, usually anywhere from 50 to 350 kW for charging light duty vehicles. Finding the best location for deploying a DC Fast charger requires balancing several factors, including availability of grid capacity, site specifics, and market demand. Subsequently, deploying the chargers requires close coordination with several players, including the EV charging network, the local utility, local permitting jurisdictions, subcontractors, and others. Sometimes, because of potential grid constraints and lack of streamlined processes among the various players involved, deployment timelines can get very long.
Once the chargers are deployed and commissioned, ensuring they are always available for customer use becomes the main objective. DC Fast chargers are sophisticated machines with several hardware and software technologies that serve various functions: dispense high-power electricity; modulate power output based on EV battery status and grid conditions; connect to and communicate with several EV makes and models; communicate with charging network operator; communicate with the customer charging app(s); payment processing; etc. As publicly available critical infrastructure, these units are sometimes subject to unexpected and harsh conditions (e.g., extreme weather events, vandalism, accidents), requiring rigorous and regular inspection and maintenance to maximize their uptime.
Tritium has played a significant role in helping us address these challenges and enhance our EV charging network. Our partnership has been invaluable. Tritium offers some of the fastest and most reliable chargers in the market. Chargers like the RT50, RTM75, and PKM150 are durable and fast, delivering speeds of up to 150 kW, which allows vehicles to get a full charge in as little as 30 minutes. The units also occupy a relatively small footprint, which makes them easier to deploy. Tritium chargers also offer seamless payment options to drivers, including convenient methods such as connecting through the EVCS app, online payment, credit-card swipe, and tap payments.
If I’m to describe our experience working with Tritium in one word, it’d be “collaborative.” Tritium has proven to be a great partner, and they have made the collaboration process smooth on all fronts. We continue to learn together, grow together, and succeed together, and we look forward to growing our partnership.
With Alan Dowdell, Head of Sales and Marketing, Enel X Way
Tritium and Enel X Way partnered to pursue a shared vision: to electrify transpiration and help enable renewable energy. Enel X Way provides EV charging at home and on the go, deploying Tritium chargers for EV drivers on the go.
Enel X Way is a subsidiary of Fortune 200 renewable energy leader the Enel Group and is dedicated to electric mobility. The company is driven by innovation and electrification to meet sustainability goals with their smart home, commercial, and public charging solutions. Enel X Way operates in 16 countries and manages more than 500,000 charge ports globally and more than 193,000 in North America.
Enel X Way’s award-winning home charging station, the JuiceBox, has been named the “best EV charger overall” by CNET, Car and Driver, Popular Mechanics, and Road & Track.
Fast charging is an essential piece of Enel X Way’s charging solutions portfolio. Alongside Level 2 charging for home or commercial use, accessible and reliable DC fast charging is needed for those unable to charge at home or who that require charging capabilities that gets them on the road sooner. Enel X Way’s comprehensive lineup of Tritium JuicePump DC fast chargers can charge EVs up to 80% in less than 20 minutes. It’s the perfect solution for fleet depots, shopping centers, restaurants, gas stations and convenience stores.
The United States White House Administration has set targets of having 50% of all new vehicle sales be electric by 2030 and is on track to install around 200,000 DC fast chargers by 2030. By deploying public and private DC fast chargers nationwide, we will support rapidly growing EV adoption. By 2025, the Enel Group will invest $22.8 billion in renewables. As a core region within the Enel Group, North America has pledged to meet ambitious goals including 475,000 EV charge ports, 5 GW of new utility-scale renewable and storage capacity, 37 MW in demand response capacity, and 155 MW of distributed energy storage capacity.
An integrated solar, storage, and EV charging solution is critical for reducing stress on electrical grids during peak hours and preventing blackouts. Renewable energy from solar panels and wind farms can generate clean energy to power EV charging stations during the day, minimizing electricity drawn from the grid. Storage can then hold excess solar or wind energy and deploy it at night or when grid demand is high.
The case for driving electric is undeniable. Transportation accounts for 29% of greenhouse gas emissions in the U.S., causing the Earth to warm at an ever-increasing pace. EVs provide zero emission transportation while decreasing dependence on fossil fuels and improving air quality in communities around the world.
Driving EVs also helps owners save money through incentives, rebates and tax credits that lower the cost of purchasing an EV and home charging station. Not to mention the perks of driving an EV, including access to HOV carpool lanes, reduced tolls, free public charging in select areas, and less vehicle maintenance.
Expanding access to DC fast charging comes with some challenges, such as determining where to install the stations. DC fast chargers must be placed in locations that are highly visited by EV drivers close to highways, shopping centers or other public locations that have ample parking space, amenities to use while charging, and adequate power supply. Stations must also be able to scale with increased demand for electric vehicles while meeting complex charging protocols that continually evolve. For this reason, Enel X Way and Tritium provide modular kW configurations that grow with your business needs. User experience is also critical. DCFC must be easy to find and use, and they need to be reliable with ample uptime.
Tritium has been an excellent DC fast charging partner that will help us meet increasing demand for fast charging and achieve our mutual goal of electrifying transportation. Pairing Tritium’s DC fast charging technology with Enel X Way’s smart charging platform delivers fast, flexible, and scalable charging solutions for our customers.
Enel X Way has historically been a leader in Level 2 charging for home and commercial applications. The addition of DC fast charging to our portfolio from Tritium has expanded the solutions we can offer to our customers while ensuring charger availability and reliability. Working with Tritium provides Enel X Way with the highest quality manufacturing, best practices for hardware installation, remote monitoring capabilities, and maintenance support.
Tritium’s CSO David Nicholl recently spoke with the organizers of the London EV show about the future of EV charging. This article was published on their website on 31 August 2023.

As the global automotive industry undergoes a profound transformation, the rise of electric vehicles has become a central focus. With the shift towards sustainability and cleaner transportation solutions, the development of fast-charging infrastructure has emerged as an enabler of this transition. To delve into the intricate landscape of EV charging and its role in shaping the industry, we had the privilege of having a Q&A Session with David Nicholl, Chief Sales Officer of Tritium, a leading name in fast-charging technology. Let’s delve into the world of electric vehicle charging with David Nicholl, shedding light on the technologies, strategies, and visions that are driving this transformative journey.
David Nicholl: The biggest trend has been a vast investment in DC fast charging across the globe. There are now around 5,000 rapid and ultra-rapid charging points in the UK alone (ZapMap) and the government is making a huge investment to build out charging infrastructure even more.
But we’ll need even more rapid and ultra-rapid chargers if we want to meet driver demands and emissions targets. New EV sales in the UK were up almost 20 percent this year (Society of Motor Manufacturers and Traders). Those drivers want to know that there will be a rapid charging station within easy reach no matter where they are. And the chargers at those stations need to be operational. The UK government recently passed a 99% uptime or reliability standard for rapid and ultra-rapid chargers. That will greatly improve charger availability, but it’s important that operators have robust service level agreements and preventative maintenance contracts in place with charger manufacturers. Preventative maintenance measures must be adhered to, and spare parts should be readily available to maintain uptime.
It’s also important that we have charging infrastructure that can work with a wide variety of utility power levels and different vehicles. Tritium uses dynamic load balancing to make the best use of grid power and to deliver optimal power to EVs that have varying charging speeds. Load balancing lets us distribute power among chargers, delivering the right amount of power at the right time without much waste, and ensuring power capacity is better utilised and assets provide a better return.
Mr Nicholl: Again, dynamic load balancing is a big advancement in DC charging for EVs. Very basically, it lets charge point operators charge more vehicles at the same time. It knows how much power each EV needs at a given time and only provides what’s needed. It dynamically distributes power to charge multiple EVs very efficiently in increments of just 1kW, saving power and making better use of the available power grid minimising unused capacity. The power grid is a huge issue here in the UK. In many places we simply don’t have robust power feeds that can support multiple rapid or ultra-rapid chargers. Distributed systems like our PKM let charge point operators install rapid chargers even where grid feeds are limited.
Today’s advanced ultra-rapid chargers like our PKM150 are also modular and scalable. That means the power can be upgraded over time, and additional charging stations can be added to meet the future demands of EV drivers. They’re also more reliable and easier to maintain. If a single module in a charger has an issue, the charger can still operate at a lower power output until the module can be investigated by a technician and if needed, replaced in minutes. Serviceability and modularity are key to building reliable charging infrastructure.
Chargers now also include easy payment options and drivers don’t have to download an app or sign up with a charge point operator to charge their cars.
Mr Nicholl: Fast charging can eliminate range anxiety if it’s widely available. If EV drivers know they’re never more than a few miles (or kilometres) from a rapid charger, range anxiety disappears. That’s why it’s crucial to build vast rapid charging networks across the world.
Availability of fast chargers is also critical to advancing EV adoption. Drivers want to know that they will be able to accessibly recharge an EV when arriving at a charging site without having to wait or think about it, much like the experience ICE vehicle drivers have. By increasing availability, and visibility, to fast chargers, drivers will gain the confidence that they can go whenever, wherever and never be stranded.
Amenities in and around charging stations will also help address range anxiety. If drivers know there’s a coffee shop or even a vending machine nearby, they’re more likely to stop at that station.
Lastly, and most importantly, chargers need to be reliable. Broken or unavailable chargers only erode the public’s confidence in EV charging and EVs.
Mr Nicholl: We conduct extensive interoperability testing with EV manufacturers across the globe to ensure that our chargers are compatible with their latest vehicles.
Now most charging infrastructure is largely compatible with most EVs on the market. Across Europe auto manufacturers are all adopting the CCS2 connector standard, while you’re seeing a split between CCS1 and Tesla’s NACS connectors in North America.
Rapid chargers like ours can use any connector. For example, most of our chargers in the UK and Europe have connectors for CCS and CHAdeMO—the Japanese standard. And in North America we’re planning on offering our chargers with CCS and NACS connectors and many Tritium chargers in the US also have CHAdeMO.
Easy payment processing will also help with charger-EV compatibility. In the early days many charge point operators had their own apps or cards, you had to be a member to use their systems. Now many charge point operators are using credit card readers so anyone can use their chargers. All of Tritium’s chargers have the option for contactless credit card readers so anyone can use them without being a member of a charging network.
Mr Nicholl: Chargers for heavy machinery see much more abuse than other chargers. They need to be robust and capable of handling that abuse. All our chargers are weather sealed to keep dust and dirt away from sensitive electronic components and undergo robust impact testing to ensure resiliency in the field. They’re also designed to be easily maintained and repaired. Heavy machinery operators should look for chargers that can take a beating and that can be rapidly repaired. They should also have service level agreements, or SLAs, to ensure their chargers can be repaired right away if they’re damaged. I think once heavy commercial operators know they can count on their chargers and their service providers they’ll make the switch. Electric machines are far less complex than their diesel counterparts and they should be much less expensive to operate and maintain. Electric machines make a lot of sense, the charging infrastructure just needs to be there.
Mr Nicholl: Commercial vehicles have much larger battery capacities than passenger vehicles. They need ultra-rapid chargers to charge up in a reasonable amount of time so they can spend more time on the road moving goods and getting work done. From a business perspective, fast charging means you can use your fleet more, and use it more efficiently.
High-power chargers need more power from the grid, which operators will have to consider. Commercial vehicle chargers will also need to be durable because they’ll see more use and abuse.
High-power commercial charging stations are necessary for commercial vehicles, there’s no way around it. They’re crucial to long-distance trucking and other commercial industries. I predict that many commercial vehicle operators will build their own charging infrastructure. We have many commercial vehicle operator customers who install chargers at their depots and offices for their commercial EVs. That lets them take control of their energy or “fuel” costs and achieve greater operational efficiency. They can even offset some of those costs with solar panels, wind turbines, on-site storage, or other forms of clean and renewable energies.
However, the number of chargers and charge locations an EV fleet needs really depends on the size of the fleet, utilisation rates of the fleet, and the dwell or idle times for the vehicles. In some cases, EV commercial fleets may not need ultra-rapid chargers if they can charge up overnight using level 2 AC chargers.
Mr Nicholl: People love to interact with vehicles and talk to experts. Shows like this can help answer their questions and can inspire them to move away from ICE vehicles.
And business owners need to see how EVs can fit into their organisations, what the advantages are. And there are a lot of advantages. EVs just aren’t cleaner and better for the environment—and let’s be honest mandated in a lot of countries—they’re also cheaper to own and operate. Shows like this can demonstrate the many advantages that EVs have over ICE vehicles and help businesses make the switch.
These shows are also a good way for manufacturers, charge point operators, and businesses to review the latest regulations around EVs and EV charging. The UK is rolling out new regulations and Europe has its own plan for rapid charging in the next five to 10 years. Businesses need to know these regulations so they can future-proof their EV charging investments.
In 1999, three University of Queensland students decided to challenge the world’s largest automakers in a solar car race across the Australian outback. They spent two years building a race car in a garage, engineering a sophisticated battery management system and ultra-compact, three-phase electric motor controller. They made every component as light as possible and entered their car, the SunShark, into the World Solar Challenge against the likes of Honda, Toyota, and Volkswagen. The students, David Finn, James Kennedy, and Paul Sernia placed 3rd and won a technical achievement award for their innovative power electronics systems.
After their success in the World Solar Challenge, the three students made their award-winning motor controller a commercial product: The Wave Sculptor 22. The controller is still used in solar racing today and in 2017 the three podium teams in both the Challenger Class and the Cruiser Class in the World Solar Challenge used the Wave Sculptor 22.
Finn, Kennedy, and Sernia went on to start an engineering consulting firm in Brisbane, Australia where they created systems to manage hydroelectric power stations, develop multi-MWh storage systems for green buildings, and even create the battery management system for James Cameron’s Deepsea Challenger mission. The three needed a memorable name for their consulting company. Dr. David Finn found it in an old chemistry book: Tritium. Tritium is a rare radioactive isotope of hydrogen. Unlike pure hydrogen, Tritium has one proton and two neutrons—three fundamental particles in its nucleus, just like the three founders.
In 2012, the Tritium team was asked to create a robust, weatherproof DC fast charger for electric vehicles. They used their experience in power electronics, solar racing, battery management systems, and engineering for harsh environments to create a compact, liquid-cooled EV fast charger. They commercialized that charger and shifted their company to focus exclusively on DC fast chargers. The liquid-cooled, weather sealed RT50 DC fast charger was Tritium’s first success. The 50kW charger was the most compact to date, measuring just 2000mm x 580mm x 270mm (78.75in x 22.8in x 10.6in).
During the following years, the Tritium team grew, expanding their range of chargers and building a factory at the company’s Brisbane headquarters. Tritium built and sold thousands of DC fast chargers around the world. In 2020, the company released their new modular line of fast chargers, which can be scaled to meet charging demands. The chargers are designed to let customers save costs on charging site infrastructure while reducing their capital investment and maintaining high charger availability and power output to vehicles.
In 2017, Tritium launched its first international office in Torrance, CA just outside of Los Angeles. The next year, the company opened an office in Amsterdam to serve the European market.
In 2021, Tritium launched a state-of-the-art testing facility at its Brisbane headquarters. The facility features one of the highest-power commercially accessible EMC testing chambers in the world. It’s designed to deliver up to 720kW of regenerative power from its integrated system with fully integrated AC and DC power feeds. The facility is used to test and develop ultrafast DC fast chargers.
In 2022, Tritium joined the Nasdaq exchange and began trading under the ticker DCFC, launching a new era for the business. The company launched a state-of-the-art manufacturing facility in Lebanon, TN the same year to help electrify America’s transportation. The factory will employ more than 500 people and is designed to produce up to 30,000 DC fast charger units per year.

Tritium continues to develop faster, higher-capacity chargers for electric vehicles and our team works tirelessly to electrify transportation around the world.
Want to receive future articles like this directly to your inbox?
In 2022 Tritium passed major milestones on the road to electrifying transportation. We joined the NASDAQ in January, met with President Joe Biden, Secretary of Transportation Pete Buttigieg, Secretary of Energy Jennifer Granholm, and more at the White House, signed multiple partnership agreements with major energy suppliers and charge point operators, expanded our executive team, and opened our new manufacturing facility in Tennessee. We hired more than 350 new employees and shipped thousands of chargers around the world and received approximately $200 million in sales orders. We look forward to making 2023 an even bigger year for Tritium and electric vehicle (EV) fast charging.
Ringing the Closing Bell at the NASDAQ
After more than 20 years as a private company, Tritium went public on January 27, 2022.
“The transport industry is being electrified, which means it is more important than ever for EV owners to have access to rapid, reliable charging infrastructure,” said Jane Hunter, Tritium’s Chief Executive Officer. “We are proud to provide this networked infrastructure to our customers. As a public company, we expect to continue to expand our product suite and global footprint.”
Meeting President Biden at the White House
President Joe Biden invited Tritium CEO Jane Hunter to the White House to meet with Secretary of Transportation Pete Buttigieg, Secretary of Energy Jennifer Granholm, former National Climate Advisor Gina McCarthy, and many other politicians. Biden spoke about his administration’s commitment to electrifying transportation and building America’s fast charging infrastructure. Jane Hunter spoke about our new Tennessee manufacturing facility and the future of Tritium in America.
“This is an exciting time for the e-mobility industry,” said Hunter. “We’ve reached a tipping point, and transportation as we know it is experiencing a history-making shift. In the process, it’s providing a bipartisan opportunity to create a new future for the benefit of all Americans. Cleaner air and more jobs — it’s a win-win, for Tritium, which will continue to lead the charge in this industry, and for Americans, who will be far more likely to choose EVs when they can charge them with ease.”
“We’re going to announce a state-by-state allocation for $5 billion in funding for these chargers so states can start making plans to build out what will become a national network of electric vehicle chargers,” said President Biden. “Tritium’s new facility is going to produce up to 30 000 of these chargers every year. They’ll use American parts, American iron, American steel, and they’ll be installed up and down the highways and corridors in our communities all across the country by union workers from the IBEW (International Brotherhood of Electrical Workers).”
Major Partnership Agreements
Tritium signed major partnership agreements with world-leading energy companies and charge point operators.
BP – Tritium signed a multi-year contract to deliver nearly 1,000 DC fast chargers to world-leading energy company BP for its BP Pulse charging networks in the United States, United Kingdom, Europe, and Australia.
EasyGo – Largest private car charging network in Ireland announced deployment of 200 Tritium DC fast chargers.
Enel X Way – US charge point operator Enel X Way agreed to purchase 250 Tritium DC fast chargers for its nation-wide charging network.
evyve – UK charging network evyve plans to install 10,000 charging stations by 2030 and placed an initial order for 350 Tritium DC fast chargers.
Osprey – UK charge point operator Osprey purchased over 250 Tritium rapid chargers to expand their UK network across 100 new charging destinations.
Wise EV – Wise EV is working with Tritium to build a charging network in the United States.
Tennessee Manufacturing Facility
In August, Tritium officially opened our new Tennessee manufacturing facility. Our first US-based EV fast charger manufacturing facility, located in Lebanon, Tennessee, will employ more than 500 people over the next five years and will play a crucial role in building America’s coast-to-coast fast-charging network.
Tritium by the Numbers
As of the date of this publication, Tritium has achieved the following milestones.
Looking to 2023
In 2023 Tritium plans to keep charging ahead in our quest to electrify transportation across the globe. Our Tennessee facility will add additional assembly lines to meet growing demand for DC fast chargers in the United States and the world. We plan to manufacture fast chargers complying with Buy America standards for America’s coast-to-coast EV charging network being built under the National Electric Vehicle Infrastructure (NEVI) program.
Tritium is also hard at work creating charging solutions specifically designed for fleet operations—light, medium, and heavy-duty commercial vehicles and rideshare cars and vans. We know fleet vehicles have different requirements than consumer and commuter vehicles. Some need to be recharged multiple times a day, others only need to be charged at night. The correct charging application for your fleet can drastically reduce capital expenditure and save hundreds of thousands in site construction costs.
Last, Tritium will continue to expand our workforce, providing jobs in manufacturing, engineering, customer success, sales, and marketing. And of course, we will continue to manufacture and deliver DC fast chargers for a wide range of applications, including highway, fleets, utilities, retail and marine. We look forward to helping our customers and the world electrify transportation in 2023.